What Is Google BERT?
BERT—which stands for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, a Natural Language Processing technique—is an algorithm that has been added to Google Search to improve the accuracy and relevance of the search results produced. On October 21, 2019, Google officially activated BERT for English-language queries and featured snippets.
BERT collaborates with previously existing Google algorithms to facilitate a clearer understanding of the searches users make by helping the system better recognize the natural language patterns people use. This enables Google Search to identify and deliver more appropriate information—results that better match the user’s input. It does not compromise or serve as a substitute for another algorithm but rather builds on the latticework foundation established by previous updates, including Fred, Possum, Mobilege, Pigeon, Hummingbird, Penguin, and Panda.
BERT understands that a single word can be interpreted multiple ways, based on context. For example, in these two phrases,
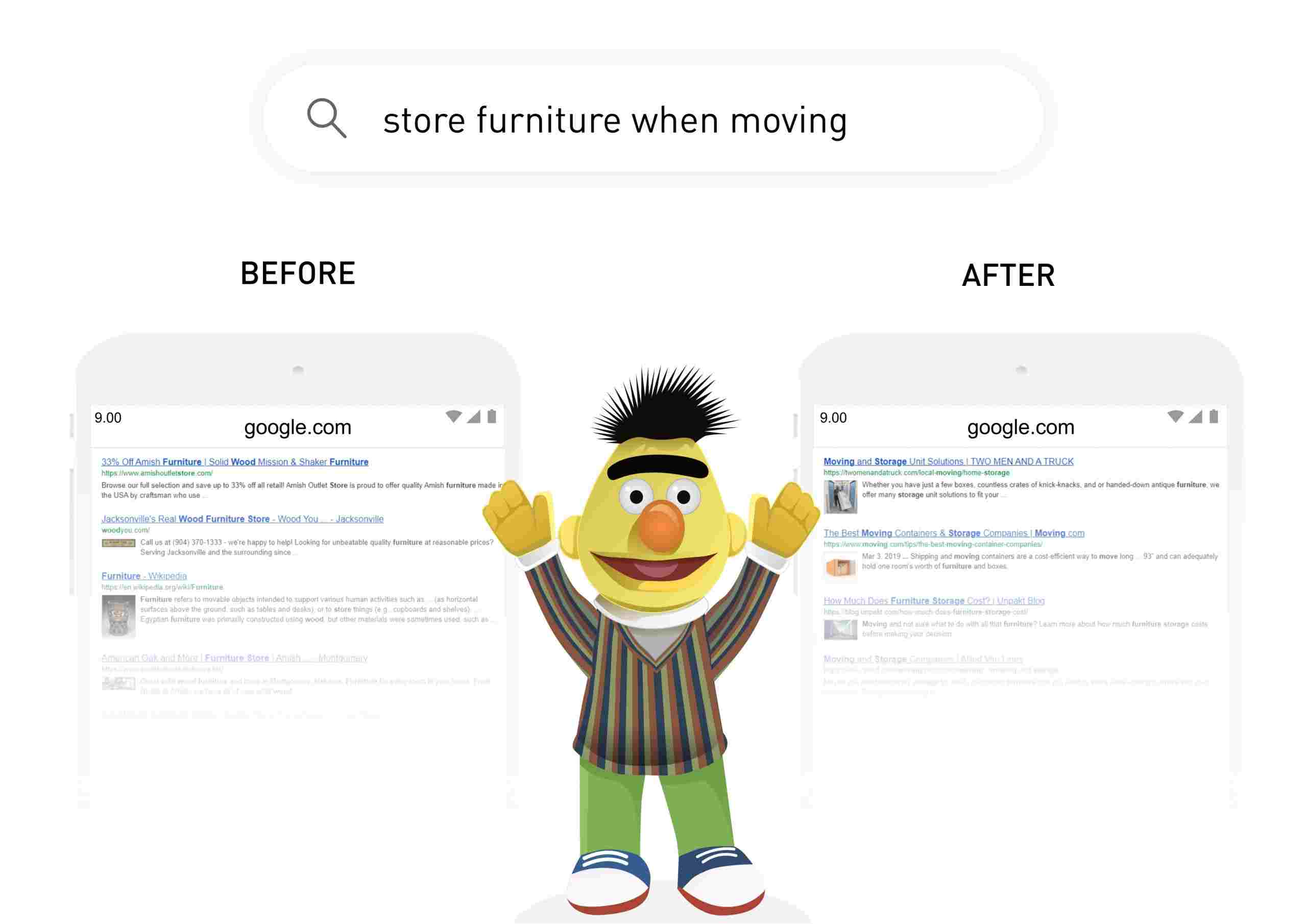
• “wooden furniture store”
• “store furniture when moving”
the word “store” has two different meanings. Although humans can easily recognize and understand the difference, a search engine would have difficulty doing so.
Google BERT has been created and implemented to discern these kinds of nuances, thereby allowing Google to provide more fitting results.
The focus, therefore, is on longer, more conversational searches in which words such as “to” and “for” are key in overall search meaning.
Google says that for the moment, the BERT update will affect (i.e., help Google Search better understand) approximately 10% of the search queries in the United States.
People using Google Search are more likely to find exactly what they are looking for—and faster. That is a good thing, of course, but what does BERT offer content creators?
As we have explained, rather than focusing on keyword density, Google will soon focus on understanding the context of users’ input text.
Up to this point, featured snippets results are offered from the first page of search results. BERT could change this pattern because feature snippets are organic, and thus affected by the new algorithm update.
Quite possibly, BERT will be able to zone in on lengthy text in pages to identify core concepts and then simply summarize the content as featured snippets, without the content creator having to optimize anything.
How Google BERT Algorithm Will Affect Website Traffic
Some content providers may see a slight uptick in the number of visitors, while others may witness a decrease. Such results will depend upon many factors. Consider monitoring other websites that rank above and below yours for the same keyword terms. You have nothing to fear if you provide high quality, relevant content on your website.
Typically, the first item on the search results page is positioned to attract the most visits. This means that the site that claims the number one spot on the first page of search results will dominate because of its contents’ relevance to what the user is trying to find.
BERT mostly affects informational queries because they involve more ambiguity than other queries. Mostly likely, SEO (search engine optimization) will no longer focus on keywords but instead on concise and relevant writing that answers users’ questions.
As we have seen with previous Google updates, the best approach is simply to keep producing solid, quality content that provides the answers users are seeking. Research traffic trends for all target keywords, and focus on users to provide what they want to know.
Ultimately, you want the answer to the question Can readers find what they are looking for in this piece of content? to be “yes” with respect to every bit of content on your site.
